E: Environment
- Challenges
- Our policy
- Responsible executive (as of April 2024)
- Organizational responsibilities (as of April 2024)
- Grievance mechanism
- Main resources for promoting activities (2023)
- Environmental accounting
- Addressing nature-related risks and opportunities (TNFD)
- Conserving water environments (TNFD)
- Contributing to the circular economy
- Preventing chemical pollution
Challenges
- Addressing nature-related risks and opportunities (TNFD)
- Conserving water environments (TNFD)
- Contributing to the circular economy
- Preventing chemical pollution
Relevant stakeholders
Direct: Local communities, the environment, customers
Indirect: Shareholders and investors, creditors, NGOs, industry groups
Our policy
Our Global Environmental Policy commits us to supporting international standards, and we adopt a precautionary approach in our efforts to help solve global climate change and other environmental challenges across the value chain.
We take early action to address environmental issues through this precautionary approach such as risk assessments to support international norms, including the United Nations (UN) Rio Declaration on Environment and Development and Agenda 21 and 10 principles of the UN Global Compact, and fulfil our responsibilities. Following the release of the final recommendations (ver. 1.0) of the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosure (TNFD) in September 2023, we started initial disclosures where practicable.
Global Environmental Policy
- Fundamental Philosophy
The Toyo Tire Group aims to create a sustainable society, where we share all-encompassing affluence and joy with everyone involved in our business. To this end, we hereby pledge to fulfill our corporate responsibility to the global environment into the future, as we seek to achieve TOYO TIRE's SDGs for resolving social issues on a global scale.
- Action Guidelines
1) We comply with international rules and laws.
We will continue to support international rules for the protection of the global environment and work to comply with environment-related laws and regulations in the countries/regions where we operate.
2) We act to mitigate the impact of the climate crisis.
Climate change is causing various critical situations (climate crises) across the planet. We acknowledge that, for us to stay in business, it is of great importance to respond to this change and whatever changes the future may bring. While contributing to the achievement of internationally-committed goals, such as curbs on energy usage and reduction in CO₂ emissions, we will lay a foundation for our business continuity that minimizes the impact on our business in the wake of natural disasters.
3) We use water with the utmost care.
We are cognizant of the importance of ensuring access to safe water (fresh water) at our premises and their surrounding areas for business continuity. Accordingly, we will not only strive to reduce our water consumption but also minimize the impact that the intake and discharge of water that we utilize for our business activities may have on the areas surrounding our premises, with the aim of creating a social environment where it is perfectly safe to use water resources.
4) We do not waste resources.
We are also cognizant of how important it is, for the sake of business continuity, to use only the necessary amount of resources, conforming to a predetermined plan, on the premise that all resources on this planet are limited. We will also contribute to the development of an enriched social structure for utilizing resources with enhanced efficiency by using precious resources effectively and without waste.
5) We continue manufacturing with considerations given to the environment and people’s lives.
In each process of the value chain, we determine if precautions are taken to conserve the environment and ensure that chemical substances are used safely. We will adhere to these measures to continue to provide products, technologies, and services that enrich the environment and the lives of people.
6) We protect the rich natural environment and people's lifestyles in places where we source our raw materials.
Being fully aware of the fact that we consume large quantities of natural rubber as raw materials for our products, we will strive to protect bountiful forests in places of its origin, as well as the lifestyles of people living there in collaboration with all involved organizations.
7) We value communications with the public.
We are cognizant of the importance that, as a corporate citizen of society, we act with a full understanding of the enduring impact that our business activities may have. Therefore, we will strive to facilitate communications and build a better relationship with the public through a series of constructive and sound dialogues with them in order to ensure that we understand ourselves better and that the public develops an unobstructed understanding of our company.
- Maintaining/Improving Management Systems
Officers and organizations in charge of safety & environment shall be held responsible for the content of this Charter and promote business activities in line with it throughout the Toyo Tire Group.
The departments in charge of implementation shall determine their action plans (targets) in accordance with the action guidelines and strive to realize the basic principles laid out in this Charter. The Environment Subcommittee of the Companywide Safety and Health Committee audits the content of the action plans and their progress annually to evaluate the outcome of such actions and, if deemed necessary, provide guidance on improvement.
Plans (targets) and their progress for matters of particular importance in the action guidelines, such as climate change, water, and resources, shall be reported periodically to the Board of Directors.
Environment Subcommittee FY2024 Priority Measures
| Measures being developed | Targets |
|---|---|
| Promote the proper disposal of industrial waste |
|
| Promote the disposal of PCB waste |
Manage the disposal of PCB waste in accordance with our plans |
| Confirm environmental issues at all sites and promote corrective measures |
Conduct audits, identify issues, and confirm corrections have been made
|
| Improve the accuracy of environmental data for disclosure |
|
| Ensure that the impact of water withdrawal and discharge on the surrounding environment is considered in the activities of all sites |
|
| Ensure thorough management of hazardous chemical substances at our sites in Japan |
|
Operational status of environmental management system
ISO 14001 certification at manufacturing sites (as of January 31, 2024)
Number of manufacturing sitess (globally): 11 ISO-certified sites: 10 (certification rate: 90.9%)
<Reference>
-
ISO 14001 certification at manufacturing sites (as of December 31, 2022)
Number of manufacturing sites (globally): 11 ISO-certified sites: 10 (certification rate: 90.9%)
Responsible executive (as of April 2024)
Corporate Officer and Vice President of the Quality Assurance, Environment & Safety Headquarters
Organizational responsibilities (as of April 2024)
- * Toyo Tire Corporation
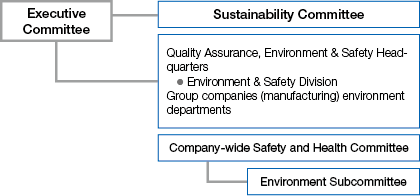
Grievance mechanism
- Reporting hotline (whistle-blowing system): For executives, employees, suppliers
- Customer Relations Department: For customers (consumers) and local communities
- Online inquiry form: For customers (consumers), shareholders and investors, and NGOs
Main resources for promoting activities (2023)
- Expenses for preventing pollution of air and water systems: 125 million yen
- Expenses for recycling resources:518 million yen
- Expenses for managing environmental activities:84 million yen
- * Adheres to the Environmental Accounting Guidelines 2005 (Japan’s Ministry of the Environment). Includes depreciation of depreciable assets.
- * Main business area: Japan
Environmental accounting
Addressing nature-related risks and opportunities (TNFD)
In 2023, the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) published version 1.0 of its recommendations and the Science Based Targets Network (SBTN) published version 1.0 of its guidance for setting Science Based Targets for Nature (SBTs for Nature). These two documents clarify the role of companies in avoiding, reducing and restoring the impact of their business activities on nature, increasing the demand on companies to take initiatives and disclose information. As a company that relies on natural capital in our business, we developed a long-term roadmap in 2023 that recognizes nature and natural capital. Going forward, we will implement initiatives at each phase in accordance with the roadmap and we will gradually disclose information in line with the TNFD recommendations.
Long-term roadmap
In 2023, we developed a long-term roadmap that recognizes the natural capital we rely on, which includes not only water resources but also sanitation and hygiene (WASH) and biodiversity. Going forward, we will take initiatives to implement each phase of the roadmap.
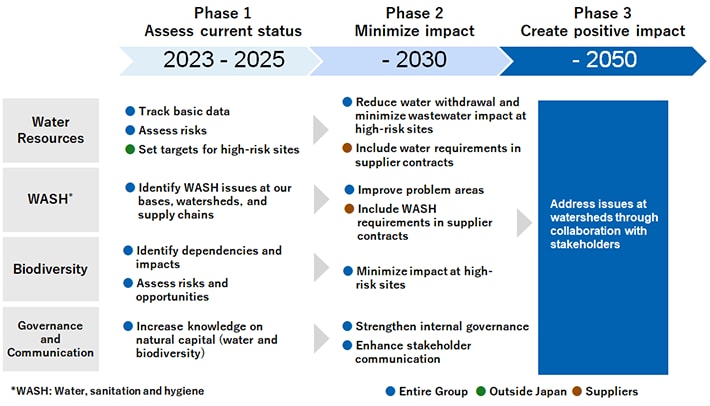
Addressing nature-related risks and opportunities
In 2023, we implemented Phase 1 (assess current status) with respect to water resources, which are essential to our business activities.
Water risk assessment
- ・Assessment indicators: Of the two Aqueduct water resource risk assessment indicators, Water Stress and Water Depletion, Toyo Tire Corporation uses Water Depletion to conduct its risk assessments because that is a more pertinent representation of the water resource situation in the basin.
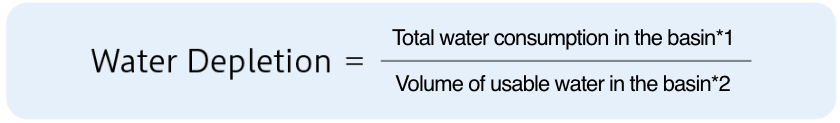
*1 Water consumption: The amount of water withdrawn that cannot be reused
*2 Volume of usable water = Volume of water resources in the basin – Volume of water consumption from the basin
- ・Assessed areas: 12 areas where the Group has manufacturing bases
- ・Assessment period: April 2023
- ・Assessment results: One high risk area in China (Zhucheng City). One medium-high risk area in Thailand. All the other areas were low risk.
Water risk targets and indicators
- ・Reduce water withdrawal by 10% compared to 2023 levels by 2030 at our bases in China which have been assessed as high risk in terms of water depletion by Aqueduct.
- ・Manage factors affecting increases and decreases in water withdrawal and continue to assess risks.
- ・Enhance data collection on water discharge volume and quality and continue to assess risks.
Reducing water risks (TNFD)
Reducing volume of water withdrawal and managing discharge appropriately
We believe it important that we conserve and make optimal use of water resources, and have set targets for reducing water use to drive Group-wide measures to save water and expand water recycling and reuse.
The Group mainly uses municipal or other public and private water supply facilities as well as groundwater for our boiler equipment and parts processing facilities, the cooling of production parts, cooling towers and welfare facilitates at our manufacturing bases. For water withdrawal and discharge, we are working on proper water-resource management throughout the Group using efforts such as improving equipment to reuse water as much as possible in each production process.
Seventy percent of the Group’s main sites, or sixteen out of 23, have developed water management plans and are implementing measures to reduce water use. As a result of our efforts over a five-year period (2019–2023) to reduce water withdrawal at our bases in Japan by 10% compared to 2018 levels, we reduced our water withdrawal in 2023 by 19%, thereby achieving our target.
Moving ahead, we will follow the long-term roadmap and continue working on our targets of reducing water withdrawals at high-risk sites as well as minimizing wastewater impacts. We will maintain appropriate water usage at major domestic and overseas bases other than high-risk bases by managing changes in water withdrawals per unit of production.
Water withdrawal
Click here to view the data for 2019-2023.
Water discharge
Click here to view the data for 2019-2023.
Management of water discharge-related impacts at our manufacturing sites
Click here to view the data for 2019-2023.
Third-party assurance:
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data that we disclose, we have obtained the assurance of a third-party organization for our 2023 environmental data.
- Verification scope: 114 sites* belonging to Toyo Tire Corporation and related companies, for total scope 1 energy-derived CO₂ emissions, scope 2 emissions, total water withdrawal, breakdown of water withdrawal, total water discharge, and breakdown of water discharge
- * Toyo Tire Corporation (Headquarters, Sendai Plant, Kuwana Plant (tire and automotive parts), Hyogo Manufacturing Complex, Corporate Technology Center, Tire Technical Center, Automotive Parts Technical Center, Miyazaki Tire Proving Ground, Saroma Tire Proving Ground, Tokyo Office, Hiroshima Office, Kanto Distribution Center, Kansai Distribution Center); Fukushima Rubber Co., Ltd.; Ayabe Toyo Rubber Co., Ltd.; Orient Machinery Co., Ltd. (Headquarters, Sendai branch, Rokko branch); Toyo Tire Japan Co., Ltd. (87 sites); Toyo Automotive Parts (USA), Inc.; Toyo Tire North America Manufacturing Inc.; Toyo Automotive Parts (Guangzhou) Co., Ltd.; Toyo Tire (Zhangjiagang) Co., Ltd.; Toyo Tire (Zhucheng) Co., Ltd.; Toyo Tyre Malaysia Sdn. Bhd.; Toyo Rubber Chemical Products (Thailand) Limited; Toyo Tire Serbia D.O.O.
- Verification period: January 2023 to December 2023
- Verification criteria: ISO14064-3: 2006, related laws and regulations, and the assurance organization’s protocol
- Third-party assurance organization: SGS Japan Inc.
Please click here to read more about verification statement.
Water consumption
Click here to view the data for 2019-2023.
In fiscal 2023, there were no legal violations related to water quality, water withdrawal or water discharge.
Contributing to the circular economy
Resource recycling
We believe it is the social responsibility of global manufacturers to make it their mission to help transition our society from one that consumes resources to one that recycles resources.
The Toyo Tire Group is using an increasing amount of raw materials as the scale of our production expands. We strive to secure a stable and sustainable supply of natural rubber, our prime raw material, and other materials at the procurement stage. At the same time, we are also working hard to promote research and development of new materials and improve product design and production processes to ensure more efficient material use. We are also in the process of evaluating sustainable materials and their usage. We are also trying to extend the life of our products by manufacturing products with excellent durability during use and turning old tires into retread tires.
Targets
Increase sustainable material*3 content to 40% by 2030 and 100% by 2050.
*3 Toyo Tire Corporation defines sustainable materials as recycled or renewable materials.
Resource recycling initiatives
- Considering the use of recycled carbon black, recycled steel, recycled bead wire and recycled polyester
- Considering the use of biomass-derived synthetic rubber, plant-based oil, rice husk ash silica and rubber powder in tire products
- Promoting the sale of retread tires
Main materials
Click here to view the data on total volumes of raw materials and sustainable material content.
High-quality Toyo Tires brand even for retread tires
The collection and recycling of used tires is an important issue for resource recycling in the tire industry. The Toyo Tire Group is striving to expand the use of retread tires as a way to address this issue.
A retread tire is a recycled used tire whose tread rubber (the rubber section that comes into contact with the road surface) has been replaced. With the exception of the tread rubber, the other parts of the tire are reused, which not only saves resources compared to new tires but also reduces CO₂ emissions at the production stage.* The energy-saving qualities can be further enhanced by using and managing them in conjunction with fuel-efficient tires. Thanks to these environmental performance features, retread tires are recognized as designated procurement items under Japan’s Green Purchasing Law.
The Group manufactures and supplies durable, high-quality tires, and users also rate our retread tires highly.
The usage history for the base tire of a retread tire is different for each tire. We supply tires that customers can use with peace of mind by building a detailed inspection system that spans the selection through to the pre-shipment of base tires and includes such checks as high-voltage inspections of damage conditions, inspections of the interior of the tires that cannot be detected from the outside, and durability checks of finished products.
We are helping promote resource recycling in the transportation industry by encouraging the spread of high-quality retread tires.
- * Assuming CO₂ emissions from the manufacturing of new tires of 100%, CO₂ emissions from retread tires are much lower at 41%. (Source: Japan Retreaders’ Association)
Number of retread tires produced (Toyo Tires branded)
Click here to view the number of retread tires produced.
How We Produce Retread Tires
There are two ways of processing retread tires: (1) a remold method in which tread rubber with no pattern is attached to a base tire, which is then placed in a mold, vulcanized and imprinted with a pattern, and (2) a pre-cure method in which patterned tread rubber is attached to a base tire, which is then vulcanized in a vulcanizer. We use high-grade technology to produce tires using both methods.

Reducing waste
- Goal: Maintain 100% recycling rate (achieved end-December 2018)
- Unit: Direct recycling volume*/total volume of waste × 100
- * Amount of waste diverted directly to waste disposal operators for recycling (excluding direct landfill volume, in-house incineration volume, and outsourced incineration volume)
- 2023 result: Recycling rate 100%
Click here to view the data on waste volumes.
Preventing chemical pollution
For necessary raw materials for continuous operations within the Group, we manage chemical substances in accordance with the laws and regulations of each market in which we operate and our business partner’s guidelines.
For instance, we have strictly managed the use, storage and disposal of specified chemical substances in Japan based on the Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL). In accordance with the Pollutant Release and Transfer Register (PRTR) system, we assess the amount of targeted chemical substances emitted or moved and register with the relevant authorities. When transferring or providing other organizations with targeted chemical substances, we provide those organizations with a safety data sheet (SDS) in accordance with the SDS system stipulated by the CSCL. We also implement any necessary responses to European Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulations, the Global Automotive Declarable Substance List (GADSL), or revisions in business partner’s lists of managed chemical substances.
We are working to maintain a 50% or higher reduction in VOC emissions compared to 2000 levels and continue to reduce them in accordance with the Japan Rubber Manufacturers Association’s voluntary action plan on reducing VOC emissions. The plan covers 17 typical substances used in the rubber industry, with rubber solvents constituting over 60% of the Group’s emissions. We have currently reduced VOC emissions by roughly 80%, far exceeding our goal, but will formulate specific plans for improving manufacturing methods and processes in efforts to reduce emissions even further.
We manage fluorocarbons, which greatly impact ozone layer depletion and global warming, in accordance with Japan’s Fluorocarbon Emission Control Law, and control leakage at less than 1,000 tCO₂.
Volumes of PRTR substances handled, released and transferred
Click here to view the data on the volumes of PRTR substances handled, released and transferred.
Ozone-depleting substance emissions
Click here to view the data on the emission of ozone-depleting substances.
VOC control targets and results
- Control targets: Reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions by 50% from 2000 baseline and continue the efforts
- Applicable operations:Toyo Tire Corporation (Sendai Plant, Kuwana Plant and Hyogo Manufacturing Complex), Fukushima Rubber Co., Ltd. and Ayabe Toyo Rubber Co., Ltd
- Unit of control: VOC emission volumes
- Fiscal 2023 result: 79.1% reduction from fiscal 2000 baseline
Nitrous oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
Click here to view the data on the volumes of NOx, SOx and VOC emissions.
Sustainability
- Message from the President
- TOYO TIRE Value creation
- TOYO TIRE Sustainability
-
TOYO TIRE Materiality
- Help create a society of sustainable mobility / Support the enjoyment of mobility for all
- Support diverse talent with motivating challenges and job satisfaction
- Continue innovating next-generation mobility technology
- Pursue decarbonization in all corporate activities
- Promote supply chain sustainability
- Ensure the fundamentals of manufacturing: quality and safety
-
ESG Activities
- E: Environment
- S: Upholding human rights
- S: Managing occupational health and safety to global standards
- S: Crisis management (responding resiliently to natural disasters, infections and other crises)
- S: Working with local communities (Helping solve local issues)
- G: Sound governance
- G: Compliance
- G: Risk management
- G: Information security
- G: Promoting digital transformation (borderless and centralized business management through ERP reform)
- External Recognition
- Report Library
- ESG Data
- ESG Data/Survey Index
- GRI Content Index
- Communication on Progress (CoP) Index
- Editorial Policy
